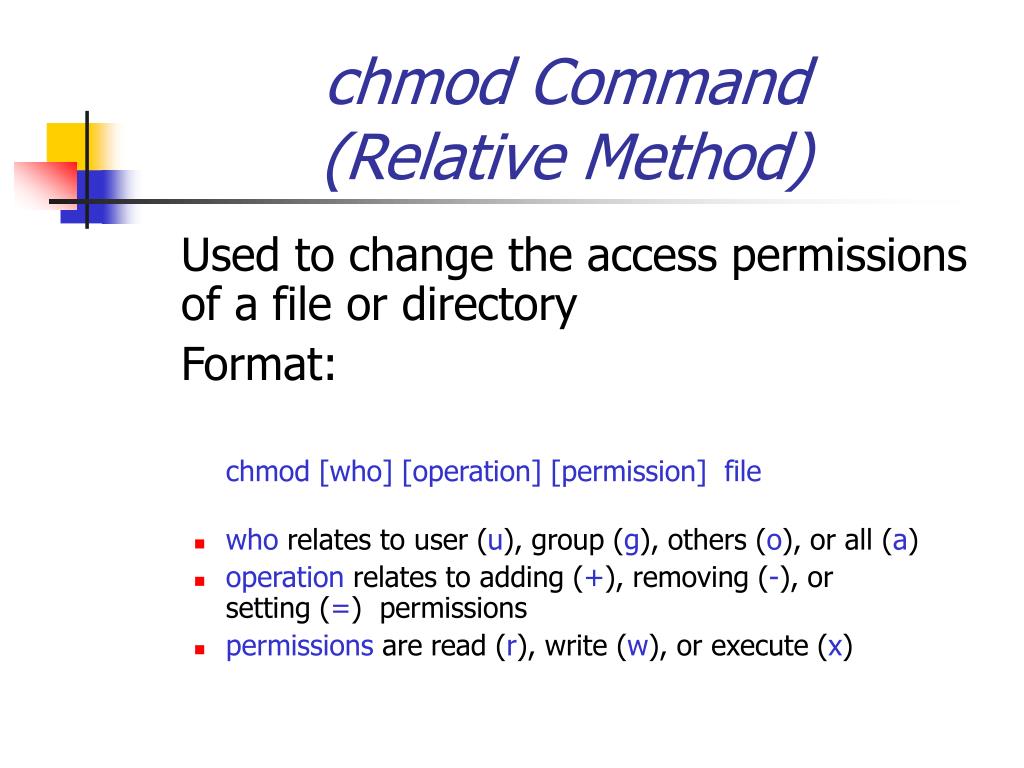
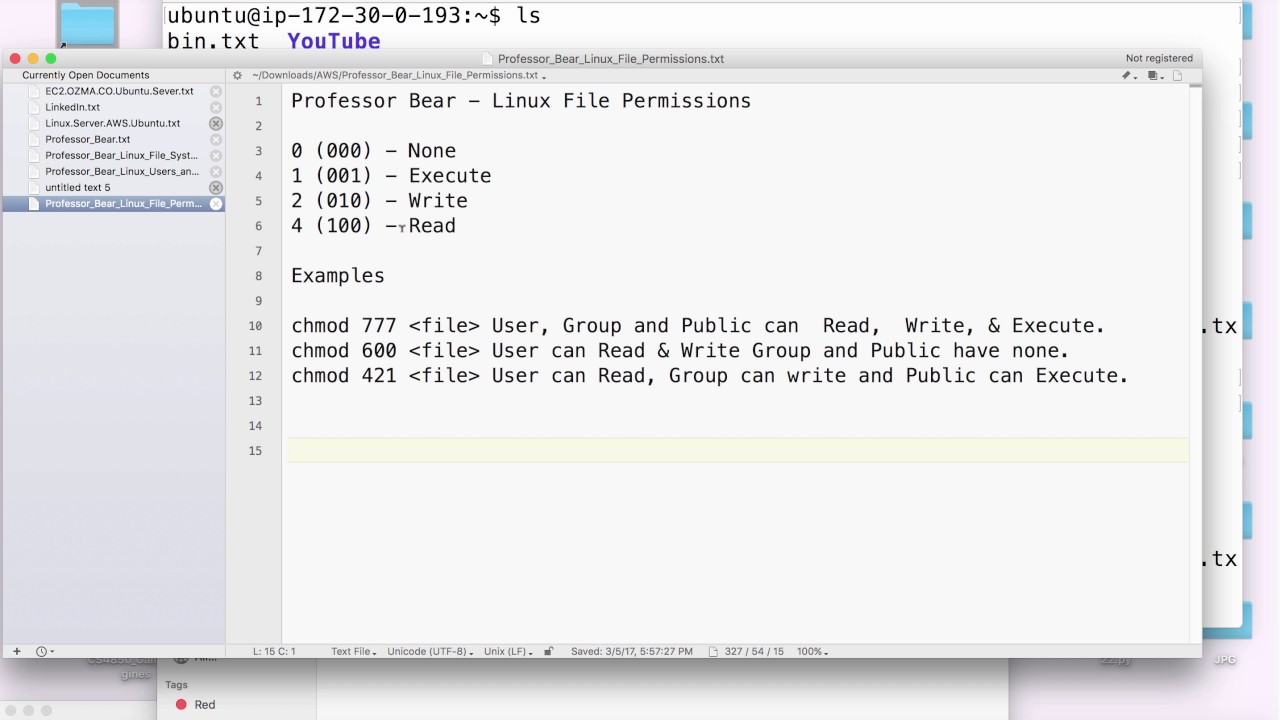
In Linux systems, "chmod" command is used to determine the access rights of users to filesIt allows us to change the access permissions of the files we specify The exact equivalent of chmod is change mode When we examine the example below;To set a file, so it is public for reading, writing, and executing, the command is chmod u=rwx,g=rwx,o=rwx file_name To set permission as in the previouslyHow do I modify that command to chmod 777 on all directories but not the files in those directories?Unix Chmod Examples 7 Chmod Command Examples for Beginners by SathiyaMoorthy on June 8, 10 Earlier we discussed about how to use octal permission bits with chmod In this article, let us review how to use symbolic representation with chmod Following are the symbolic representation of three different roles u is for user, g is for group

Comandos Terminal Chmod 777 775 600 Youtube
Chmod 777 command in unix example
Chmod 777 command in unix example-Chmod ( Change Mode ) is a command line utility in Unix , Linux and other Unix like systems to change the read, write, execute permissions of a file for owner , group and others How to use chmod?Example 5) Assign Execute Permissions to File and Group Owner $ sudo chmod ugx filename The above command adds execute permissions to the owner and the group of the file Using our file, this becomes $ sudo chmod ugx file1txt Example 6) Assign different permissions to file, group and others $ sudo chmod u=rwx,g=rw,o=r filename


Ppt Agenda Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Others can read only" chmod R 755 myfiles Recursively (R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755 User can read, write, and execute;Chmod commands on file appletxt (use wildcards to include more files) Command Purpose;Without the mask the system would set permissions of 666 for files and 777 for directories when first created The values in the mask are subtracted from these values to give a default value for access permissions for the files and directories created by you For example 777 (system value for directories)077 (value of the umask) —
# alias chmod='chmod preserveroot' and also add this to your /etc/bashrc or individual user's bashrc file for permanent changes Now if we use chmod, it does not allow to modify root permission # chmod c recursive 755 / chmod it is dangerous to operate recursively on '/' chmod use nopreserveroot to override this failsafe Linux Permissions SyntaxChmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=r myfile This example uses symbolic permissions notation The letters u, g, and o stand for " user ", " group ", and " other " The equals sign (" = ") means "set the permissions exactly like this," and the letters " r ", " w ", and " x " stand for "read", "write", and "execute", respectivelyIn such cases, the chmod recursive option (R or recursive) sets the permission for a directory (and the files it contains) The syntax for changing the file permission recursively is chmod R permission directory Therefore, to set the 755 permission for all files in the Example directory, you would type sudo chmod R 755 Example
Chmod is a program responsible for modifying access permissions of file and directories in Unix/Linux While the concept is easy to understand, the syntax might overwhelm new users a little bit Most of the time, you will encounter chmod 777, chmod 755 and chmod 644 In this article, we will explain the meaning of these numbers and how they are related to the actual permissionsChmod is only usable by the root user or the owner of the file itself chown is only usable by the user root Reason for this is that you could just create a file, put the suid bit onto it and chown it to root and voila root access is yours Also when quotas are in useWithout the mask the system would set permissions of 666 for files and 777 for directories when first created The values in the mask are subtracted from these values to give a default value for access permissions for the files and directories created by you For example 777 (system value for directories)077 (value of the umask) —



Comandos Terminal Chmod 777 775 600 Youtube



Ananth Chellathurai S Walk On Software Few Must Know Unix Commands
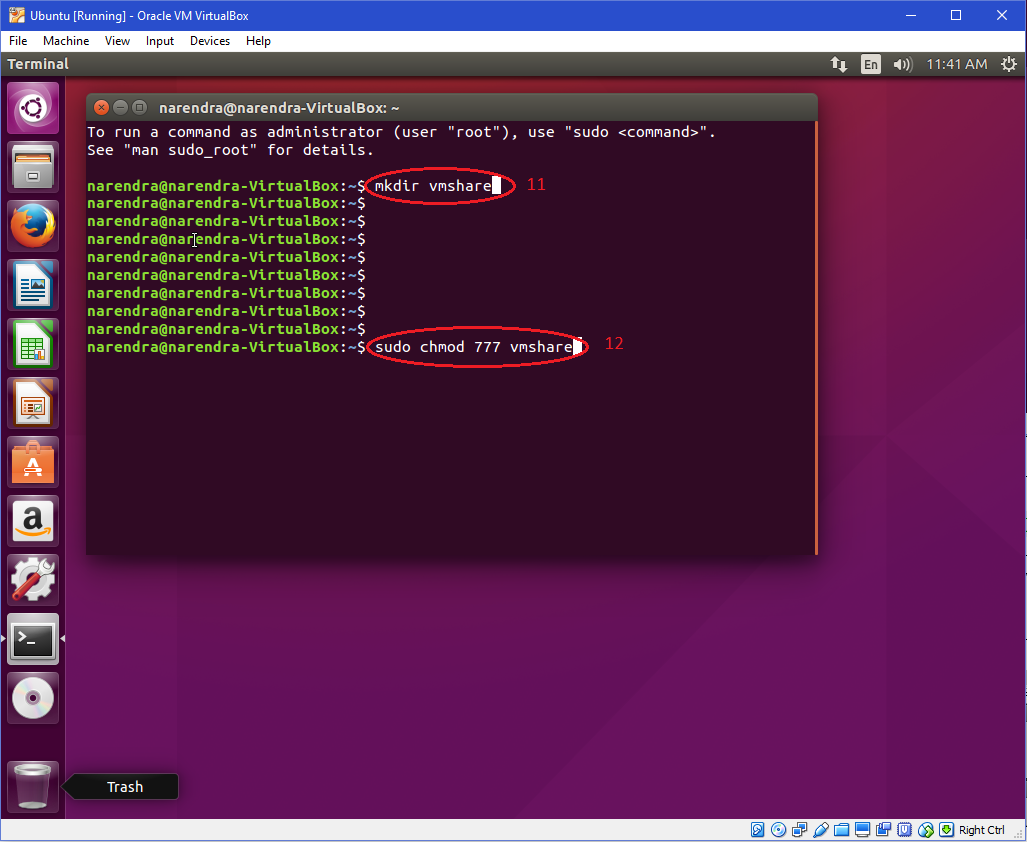
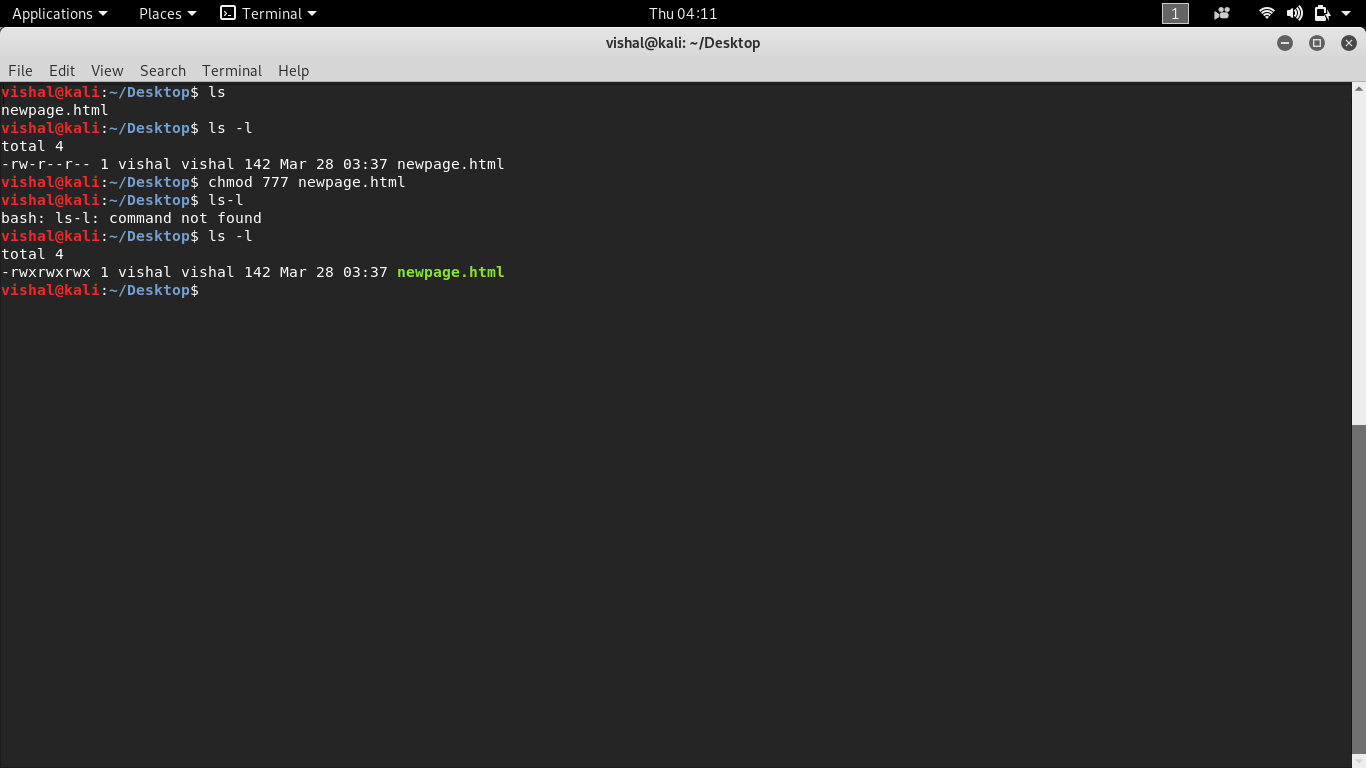
To modify these permissions, click any of the little arrows and then select either "Read & Write" or "Read Only" You can also change permissions using the chmod command in the Terminal In short, "chmod 777" means making the file readable, writable and executable by everyone chmod 777 / path / to /fileI had to chmod 755 on cgi files in those directories and I did that using this command find name "*cgi" exec chmod 755 {} \;Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write



Unix Linux Cheat Sheet By Caio Zanolla Issuu



How To Chmod Recursively In Linux Youtube
Example Say we want to grant the group execute permissions That command would look as follows chmod gx file After calling the chmod command and specifying what permissions to change for who, we end with including what file we're making the changes for If we want to use number format, that middle argument changesChmod command is used in two ways 1 Using octal value & position Sets the permission for owner, group and others with octal values , 4 for read , 2 for write , 1 for execute andUNIX Basic commands chmod The chmod command changes the access mode of one file or multiple files Syntax The syntax for the chmod command is chmod option mode files Example chmod 751 tech chmod u=rwx, g=rx, o=x tech chmod =r tech * Please note that there are many flavors of UNIX, so if in doubt, consult your man pages



Linux Chmod Recursive How To Change File Permissions Recursively



How To Run Unix Shell Command In Java Like Chmod Mkdir Grep Or Any Unix Commands Javaprogramto Com
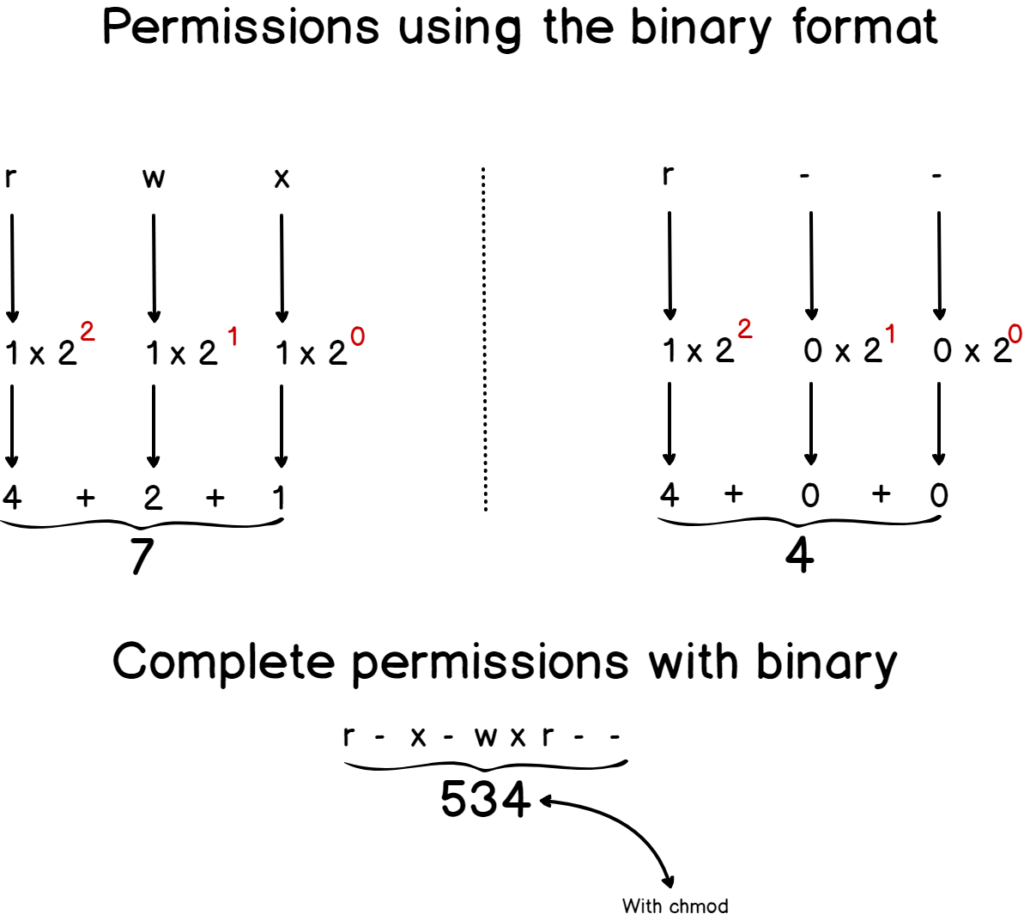
Chmod Examples in Linux / Unix 1 Give read, write and execute permissions to everyone Read, write and execute 421=7 $ chmod 777 samplesh In the above example, you can see that the permissions are specified with a three digit number The first digit is for user permissions, second is for group and third is for others permissionSuc h chmod 77 example involves Scripts What do you mean by Chmod 777?Never Use chmod 777 # Setting 777 permissions to a file or directory means that it will be readable, writable and executable by all users and may pose a huge security risk For example, if you recursively change the permissions of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www directory to 777 , any user on the system will be able to create, delete or modify files in that directory



Self Study Record Linux Command User Authority Management Programmer Sought



Chmod File Permissions In Linux Unix Linux Angular Angular Js Jquery Php Mysql And Web Development Tutorials
How to change your file to 777 or rwxrwxrwx using chmod Chmod is a well known command line utility, that's used to manage file permissions on MacOS, Linux and other Unix like operating systems While there are multiple ways to use chmod, on this site, we have chosen to focus exclusively on using chmod with Octal NotationThe permissions passed as an argument to chmod are specified as an octal value Each numeral in the value represents three bits Each numeral in the value represents three bits If three numerals are given, you're setting the read, write and execute bits for the file's owner, group and others (everyone else)Chmod 777 Example 12 "chmod go r" Command chmod go r filename * (*) gives permission to read all files that start with the trial with wildcard parameter by the group and other (other) users
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)


How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux



Docker Got Permission Denied While Trying To Connect To The Docker Daemon Socket At Unix Var Run Docker Sock Stack Overflow
For example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence chmod 1755 participants With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's readandwrite group permissions$ chmod ur,gx filename 3 Remove permission from a file/directory Following example removes read and write permission for the user $ chmod urx filename 4 Change permission for all roles on a file/directory Following example assigns execute privilege to user, group and others (basically anybody can execute this file)Chmod Examples in Linux / Unix 1 Give read, write and execute permissions to everyone Read, write and execute 421=7 $ chmod 777 samplesh In the above example, you can see that the permissions are specified with a three digit number The first digit is for user permissions, second is for group and third is for others permission


Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected



Linux Common Commands Tutorial And Use Examples Linuxcommands Site
Hello Everyone One of our admins here accidently ran chmod R 777 in the /usr folder on a V440 running Solaris 9 After that no one could run any command and could not login I fixed most of the things by rerestricting some rights and applying the correct rightsView (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 777 (chmod arwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily CHMOD Calculator Chmod 777 After changing a file's mode to 777 the file's mode will be displayed in Unix style file lsting as rwxrwxrwxIf you want to change the mode to 777, you can use the command like this chmod 777 filename chmod 777 is considered potentially dangerous because you are giving read, write and execute permission on a file/directory to everyone (who is on your system) You should totally avoid it chmod x or chmod ax Execution for everyone



Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube



Bash Sudo Abc Sh Command Not Found Ask Ubuntu
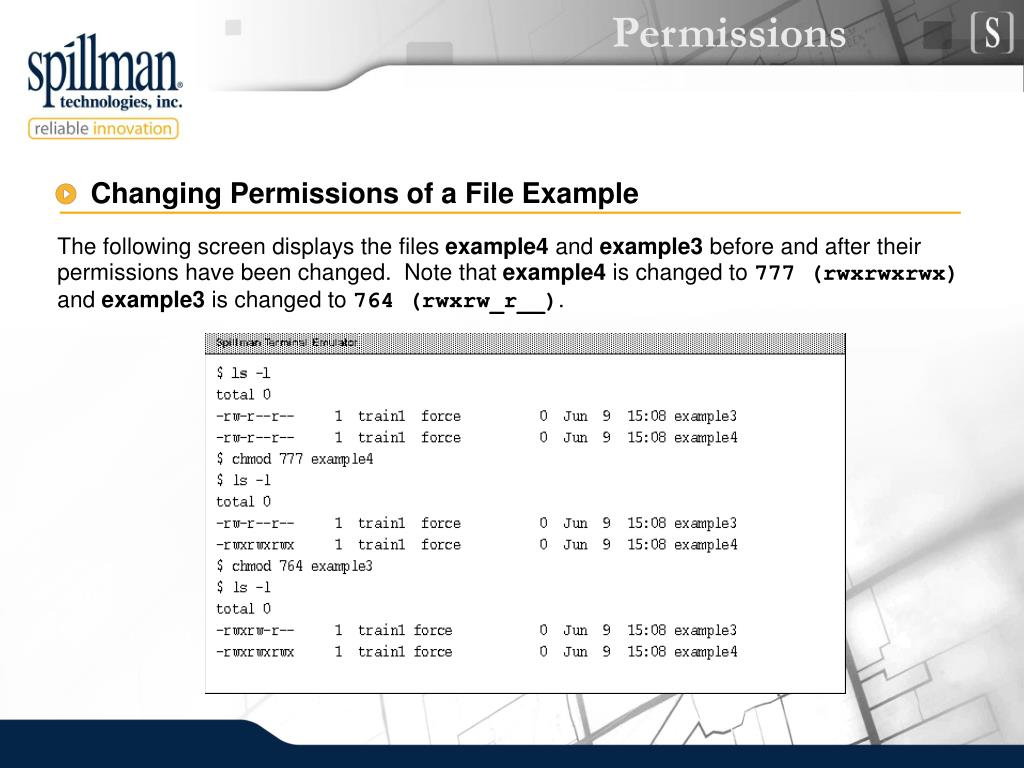
To have combination of permissions, add required numbers For example, for read and write permission, it is 42 = 6 3 chmod Examples Give read, write and execute to everybody (user, group, and others) read, write and execute = 4 2 1 = 7 $ chmod 777 filetxt (or) $ chmod ugorwx filetxt Give execute privilege to userNow, let us see how chmod command can be used to change the access mode of a file Example 1 Let's change the assgn1_clientc permission so that the owner cannot write(w) in the file but can only read it BEFORE rwrwr mik mik assgn1_clientc COMMAND chmod u=r assgn1_clientc AFTER rrwr mik mik assgn1_clientc BeforeIn the Unix system, each number code represents the permission or restriction commands That means, different numbers or number combination indicates different permissions They are related to any file



Error Running The Tutorial Example Issue 8 Jderobot Detectionstudio Github



Xoru Blog Learning About Vulnerabilities Through Apache Logs By Bas Groothedde
Examples To remove write permission from orgcht chmod w orgcht;In Unix and Unixlike operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories)It is also used to change special mode flags The request is filtered by the umaskThe name is an abbreviation of change mode Modes are the filesystem permissions given to "user", "group" and "others" classes to accessGroup can read only;
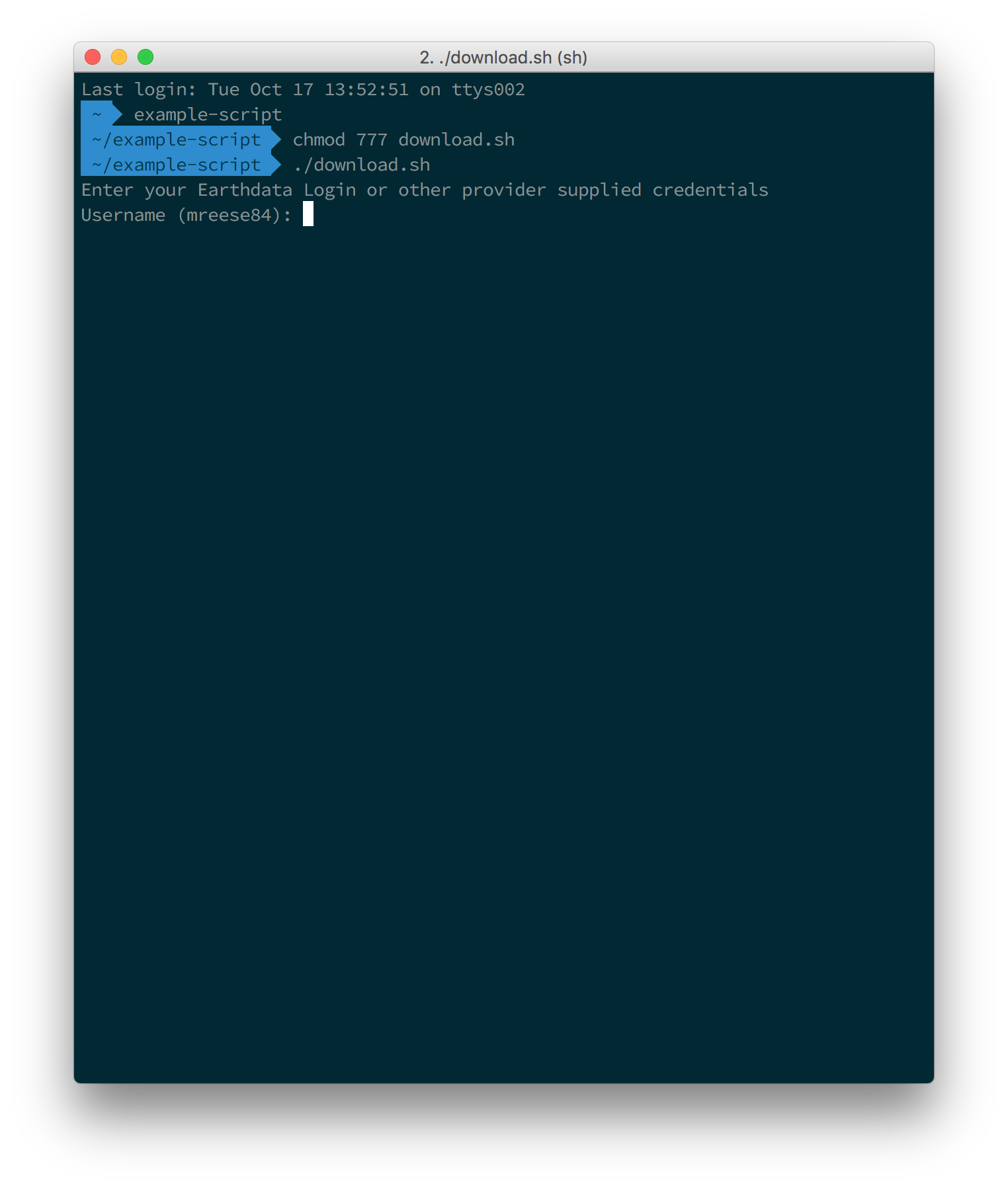


How To Use The Download Access Script Earthdata Search Earthdata Wiki



Oracle Unix Commands Unix Software Areas Of Computer Science
Chown h %U%G '%n';" \ ssh user@yourdevelopmentmachine This will take some time to run This has a good chance of fixing a large number of the 777'd permissions on your Ubuntu box However, even in the best case you should expect that you will encounter more permissionsrelated errors that you will need to fix manuallyChmod 777 Example 12 "chmod go r" Command chmod go r filename * (*) gives permission to read all files that start with the trial with wildcard parameter by the group and other (other) usersChmod 700 appletxt Only you can read, write to, or execute appletxt chmod 777 appletxt Everybody can read, write to, or execute appletxt chmod 744 appletxt Only you can read, write to, or execute appletxt Everybody can read appletxt;


Windows Powershell Chmod Command



Command Of The Day Chown Drt Sh Execute Your Inner Shell
What is chmod ?Type chmod 777 * to change mode for all files in that directory If you only want to change mode for a special type of file your can use chmod 777 *txt *dat orchmod 777 filenameext FTP In this example we're going to use WS FTP, but you can use any other FTP software that support chmod UNIX$ chmod 0 sampletxt Write by anyone $ chmod 002 sampletxt Execute by owner only $ chmod 100 sampletxt Execute by group only $ chmod 010 sampletxt Execute by anyone $ chmod 001 sampletxt Allow read permission to owner and group and anyone $ chmod 444 sampletxt Allow everyone to read, write, and execute file $ chmod 777 sampletxt



How To Set Chmod 777 To A Folder And All Its Contents Dev Community



Shell Scripting Tutorial 10 Change File Permissions Using Chmod Youtube
Example Say we want to grant the group execute permissions That command would look as follows chmod gx file After calling the chmod command and specifying what permissions to change for who, we end with including what file we're making the changes for If we want to use number format, that middle argument changesView (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 777 (chmod arwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily CHMOD Calculator Chmod 777 After changing a file's mode to 777 the file's mode will be displayed in Unix style file lsting as rwxrwxrwxSo if you want to recursively change the permission of all the files of example directory to 777 then you need to use chmod R 777 example command as shown below root@localhost ~# chmod v R 777 example mode of 'example' retained as 0777 (rwxrwxrwx) mode of 'example/hellors' changed from 0644 (rwrr) to 0777 (rwxrwxrwx) mode of 'example/hello' changed from 0755 (rwxrxrx) to 0777 (rwxrwxrwx)



File Security And Access Control Ppt Download



Linux Cheat Sheet
Chmod Examples in Linux / Unix 1 Give read, write and execute permissions to everyone Read, write and execute 421=7 $ chmod 777 samplesh In the above example, you can see that the permissions are specified with a three digit number The first digit is for user permissions, second is for group and third is for others permissionThe permissions passed as an argument to chmod are specified as an octal value Each numeral in the value represents three bits Each numeral in the value represents three bits If three numerals are given, you're setting the read, write and execute bits for the file's owner, group and others (everyone else)In the Unix system, each number code represents the permission or restriction commands That means, different numbers or number combination indicates different permissions They are related to any file



How To Use The Download Access Script Earthdata Search Earthdata Wiki


Directory Permission 777 For Mac
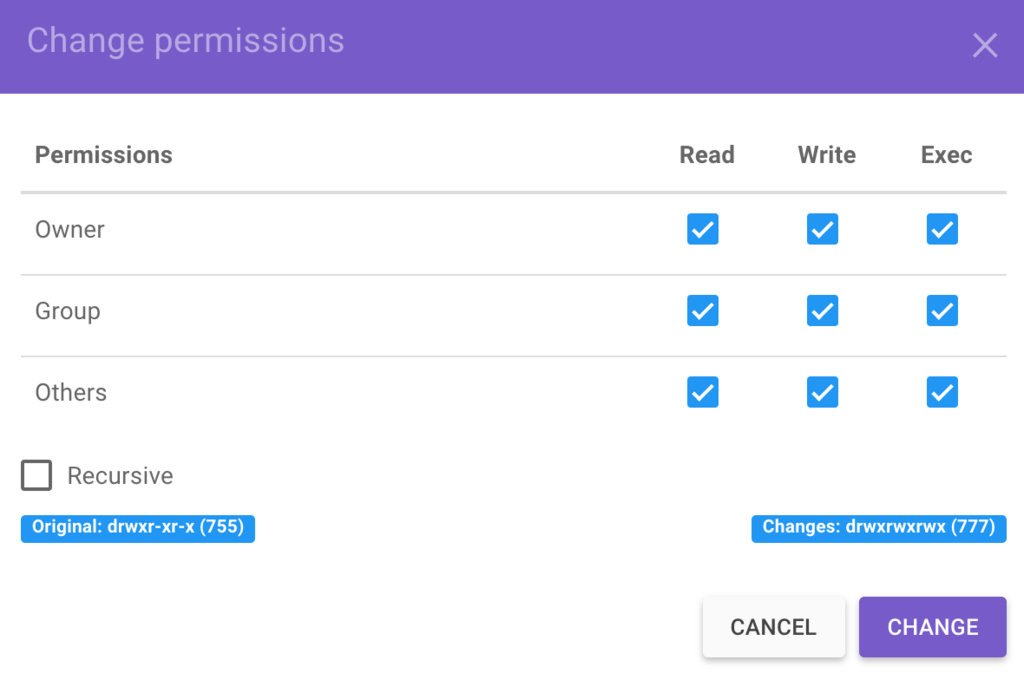
So if you want to change the permission of directory example from 0755 to 0777, you need to use chmod v 777 example command as shown below root@localhost ~# chmod v 777 example mode of 'example' changed from 0755 (rwxrxrx) to 0777 (rwxrwxrwx)Sudo find / print0 \ xargs 0 stat c "chmod %a '%n';Re chmod 777 access to a file Posted 1215 PM ( views) In reply to Tal The surest way is to set it after the file has been written, either with the x statement, or the filename pipe method



Self Study Record Linux Command User Authority Management Programmer Sought



Agenda The Linux File System Chapter 4 In Text Ppt Download
Suc h chmod 77 example involves Scripts What do you mean by Chmod 777?If there are no other directories, other than the ones you wish to operate the chmod command on, in /home/domains you can issue this command find /home/domains/*/ type d exec chmod 777 {} \;Full control over file attributes is available in Java 7, as part of the "new" New IO facility ()For example, POSIX permissions can be set on an existing file with setPosixFilePermissions(), or atomically at file creation with methods like createFile() or newByteChannel() You can create a set of permissions using EnumSetof(), but the helper method PosixFilePermissionsfromString() will



人気ダウンロード Chmod 777 Example ただの車



Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
Command Examples To change the permissions of the file participants so that everybody has full access to it, enter chmod 777 participants The first 7 sets the permissions for the user, the second 7 sets the permissions for the group, and the third 7 sets the permissions for everybody elseThe command executed here is chmod 777 R home and it gives 777 permission to the folder home itself, also to all of the files and subdirectories inside this folder The format of the command is chmod XXX R directorylocation You might also require to run this command as sudo userExamples chmod 644 filehtm Set the permissions of filehtm to "owner can read and write;



Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions


印刷可能 Chmod 777 Command In Windows ただの車
In Linux systems, "chmod" command is used to determine the access rights of users to filesIt allows us to change the access permissions of the files we specify The exact equivalent of chmod is change mode When we examine the example below;To set a file, so it is public for reading, writing, and executing, the command is chmod u=rwx,g=rwx,o=rwx file_name To set permission as in the previouslyChmod ow file2 You can combine multiple references and modes to set the desired access all at once For example, to explicitly make file3 readable and executable to everyone chmod ugo=rx file3 The all (a) mode is the same as ugo, allowing the previous command to be expressed as chmod a=rx file3Which will chmod all the directories under all the directories under /home/domains/domains1100 if you get what I mean Another way to do it is to make a file which contains all the directory names under /home/domains under which you want the directories chmodded which you may have if this is a



What Does Chmod 777 Mean In Linux Youtube



Ppt Agenda Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
To set all permission bits on (anyone can read/write/execute) chmod 777 scratchTo turn on read, write, and execute permissions, and turn off the setuserID bit, setgroupID bit, and sticky bit attributes This is equivalent to chmod 0777 aprsal chmod a=rwx aprsal;



Unix Permissions File Permissions In Unix With Examples


Ppt File And Directory Permissions Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Linux Common Commands Tutorial And Use Examples Linuxcommands Site



Unix 教學 Ppt Download



Chown



Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Towards Data Science


Solved Java Lang Illegalstateexception Driver Not Executable On Mac Total Qa



Bash Sudo Abc Sh Command Not Found Ask Ubuntu



Linux Common Commands Tutorial And Use Examples Linuxcommands Site
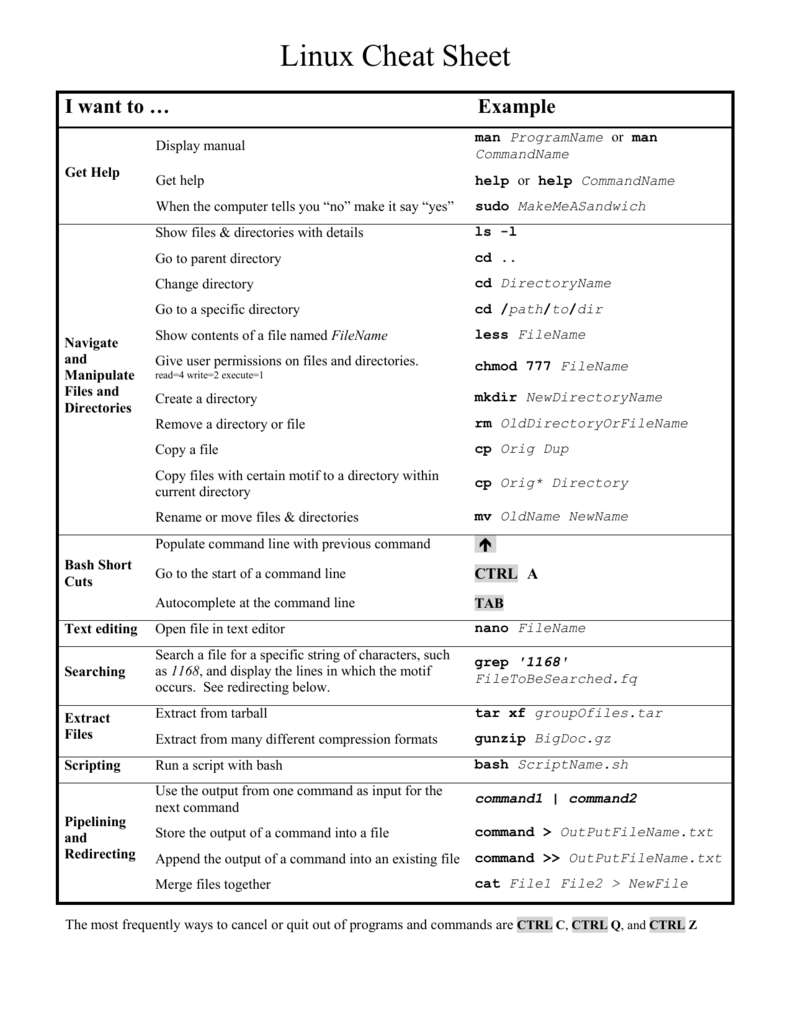


Linux Cheat Sheet



How Do You Chmod On Osx Macrumors Forums


Chmod X Windows Nativeyellow



Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather



How To Set Chmod 777 To A Folder And All Its Contents Dev Community



Unix Workshop Part3 Doc



Console Commands Utility Software Computer Data



Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet Kalitut



Bif703 File Permissions Ppt Download
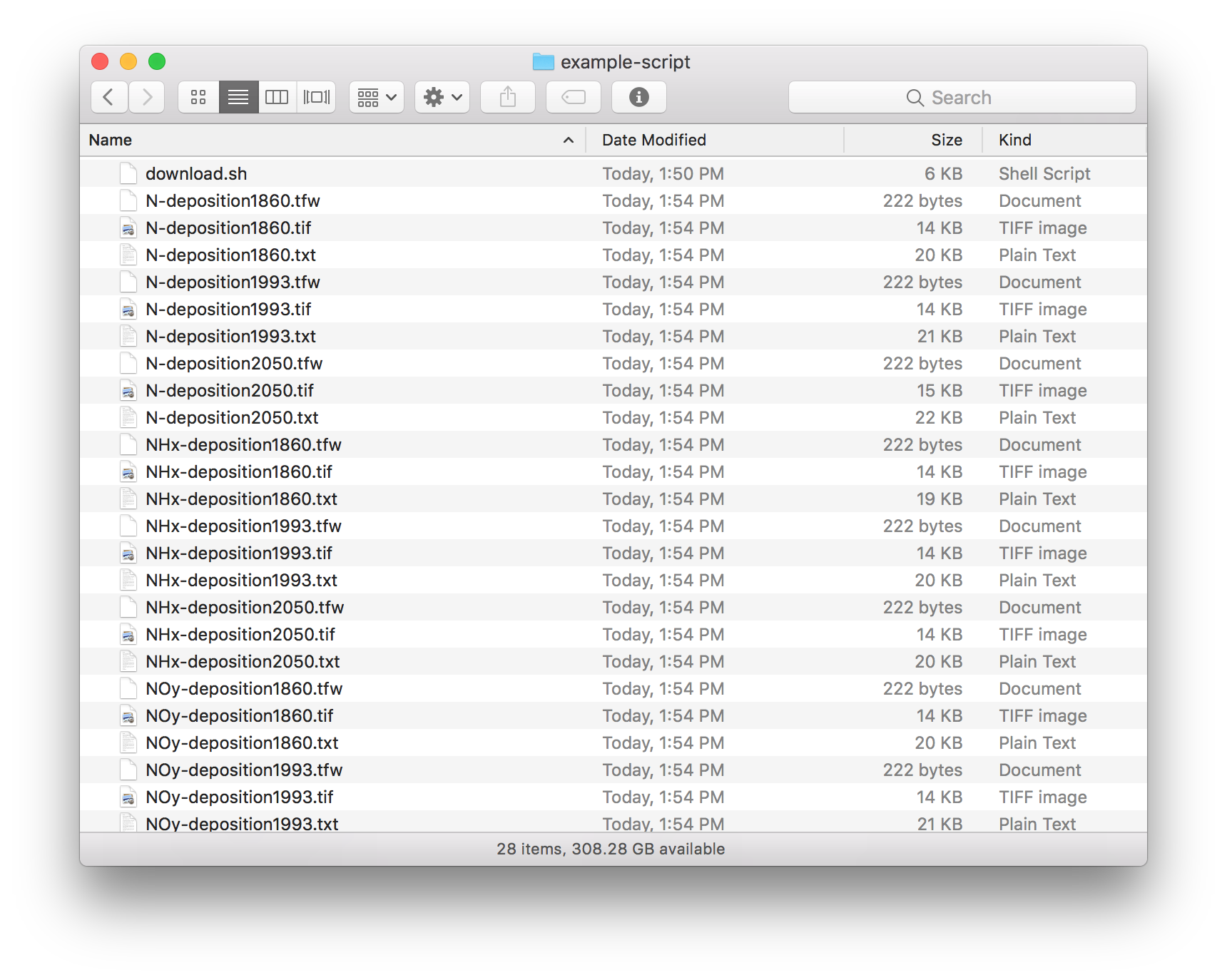


How To Use The Download Access Script Earthdata Search Earthdata Wiki
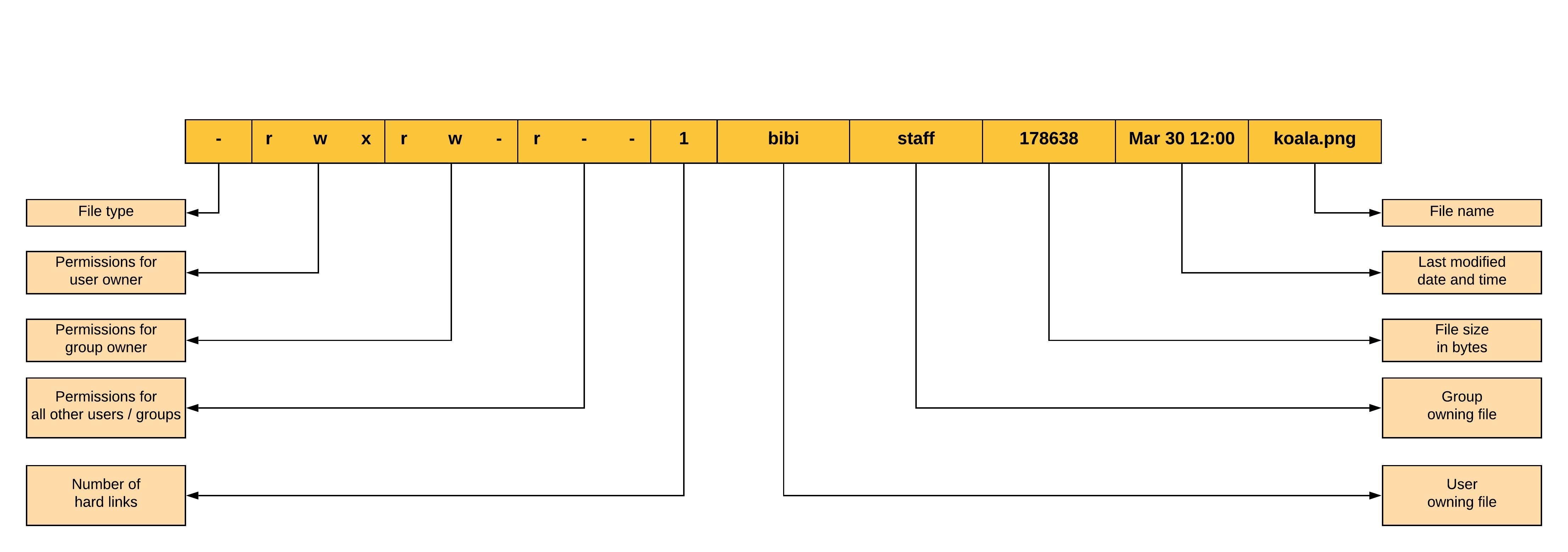


Linux File Permissions And Ownership By Udara Bibile Level Up Coding



Java Jsch Example To Run Shell Commands On Ssh Unix Server Journaldev



Directory Permission 777 For Mac



What Does Chmod 777 Mean In Linux Youtube


Unix Permissions Explained



File Security And Access Control Ppt Download



What Is Chmod 777



6 Best Linux Unix Command Cheat Sheet Linux Computer Coding Kids Computer
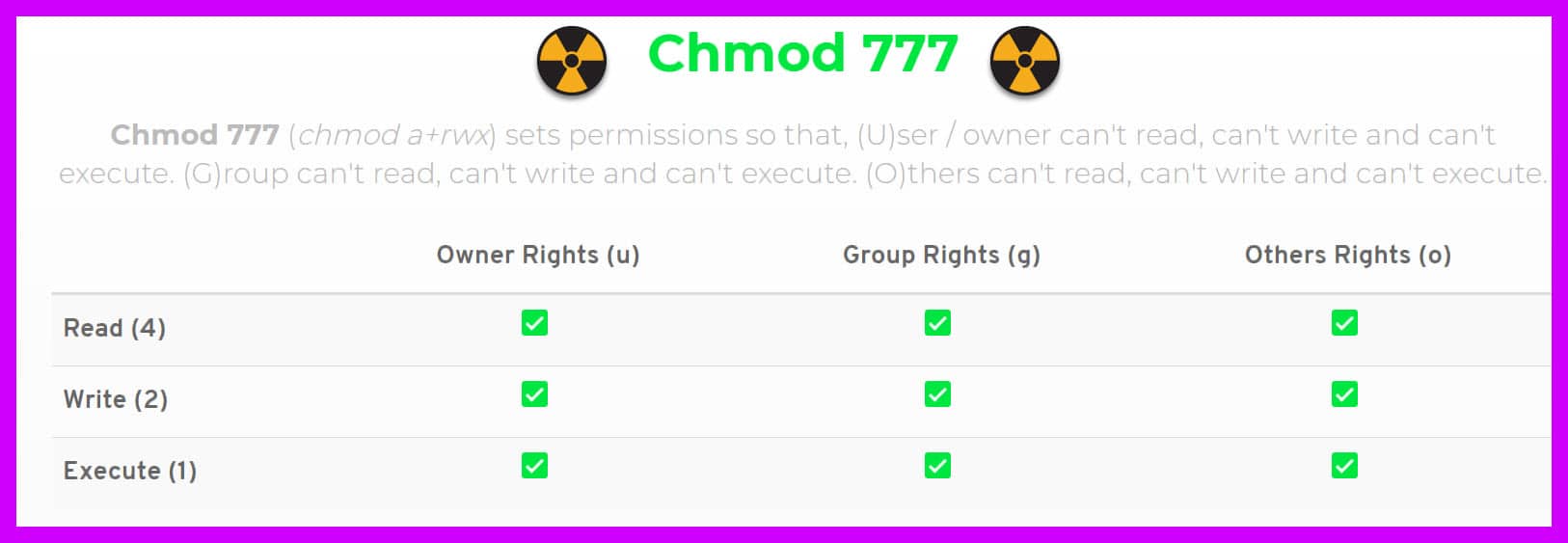


Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions



上 Chmod 777


Chmod X Windows Nativeyellow


A Handy Wallpaper Of Cli Commands 1280x1024 Linux


コンプリート Chmod Tableau



45 Linux Ideas Linux Hacking Computer Computer Programming



A Bitesize Unix Tutorial With Pixel Art By James Scott Medium



How To Manage File Permissions On Ubuntu Server 04 Dev Tutorial



Unix Linux How To Restrict To Run Commands In Specific Directory Through Sudoers Youtube



A Bitesize Unix Tutorial With Pixel Art By James Scott Medium



Basic Linux Commands Linux



Give Write Access Chmod 775



How To Create New Users Groups In Linux Cloud Network


人気ダウンロード Chmod 777 Example ただの車


Some Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Linux


Unix Commands Basic To Advanced Unix Commands With Example



Quota Cannot Impose Its Rules Unix Linux Stack Exchange



Chmod 777 What Does This Really Mean Elitehacksor



What Does Chmod 777 Mean In Linux Youtube
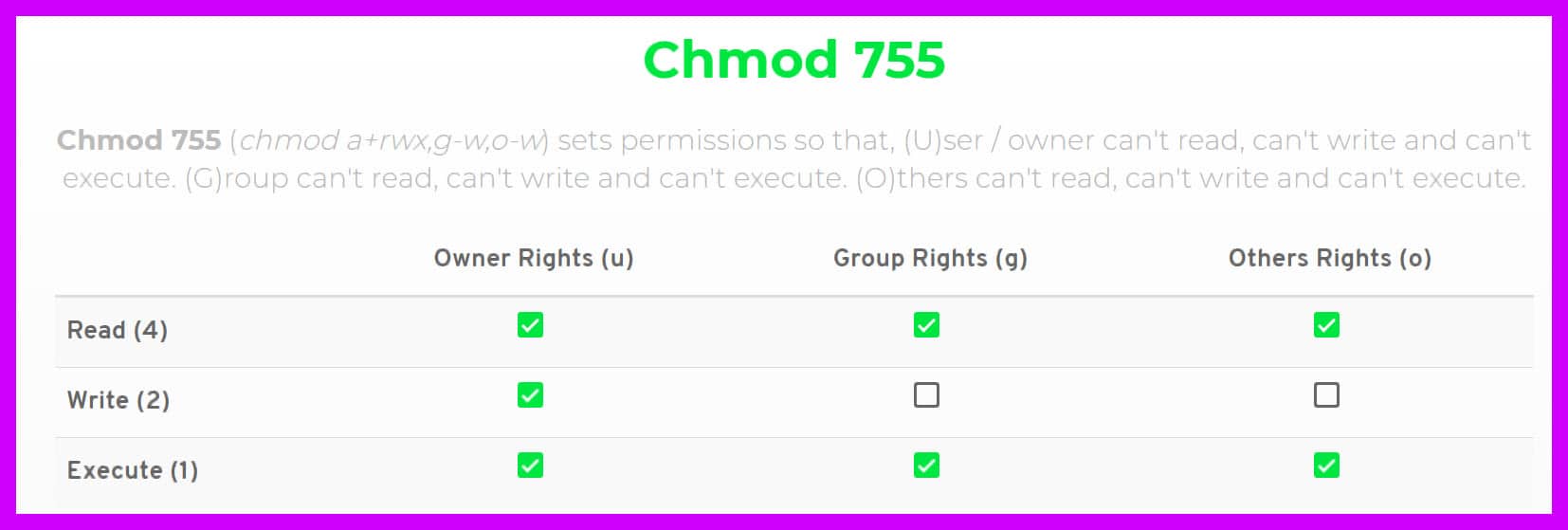


Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions



Chmod Code Example



Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu
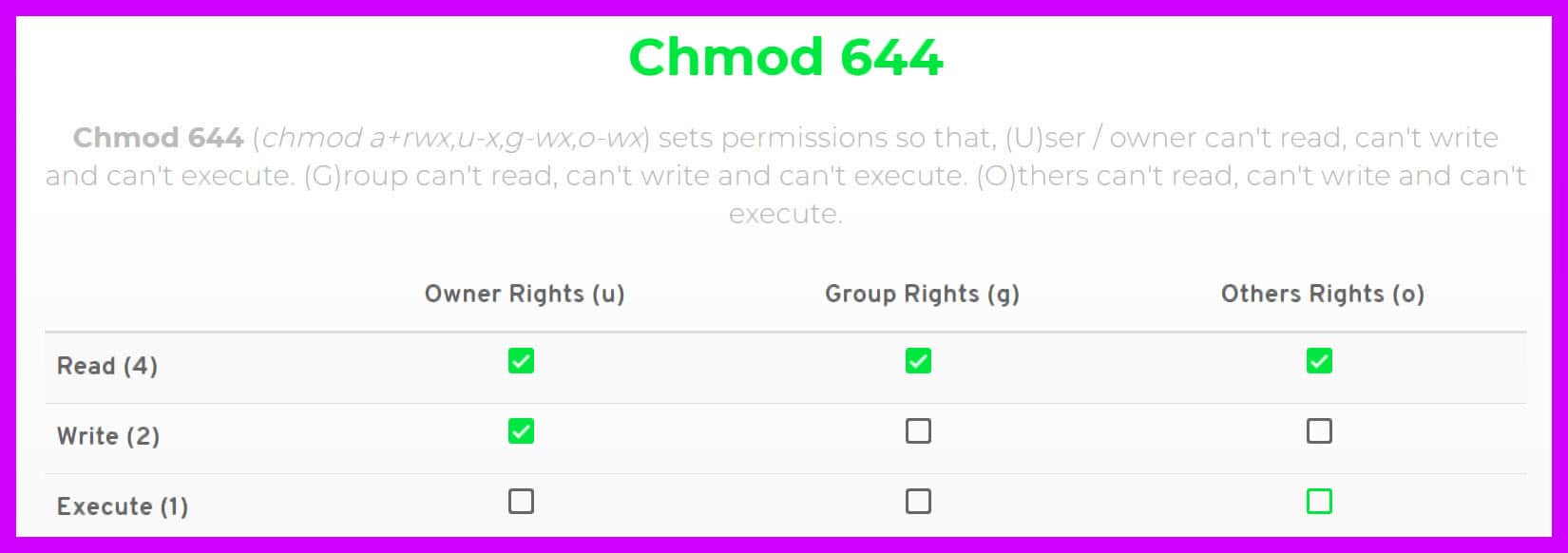


Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions


Cifs And Chmod 777 Truenas Community



In The Last Class Ls L Command Seven Fields Ppt Download



Ppt File And Directory Permissions Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



The Chmod Command And Linux File Permissions Explained



A Bitesize Unix Tutorial With Pixel Art By James Scott Medium
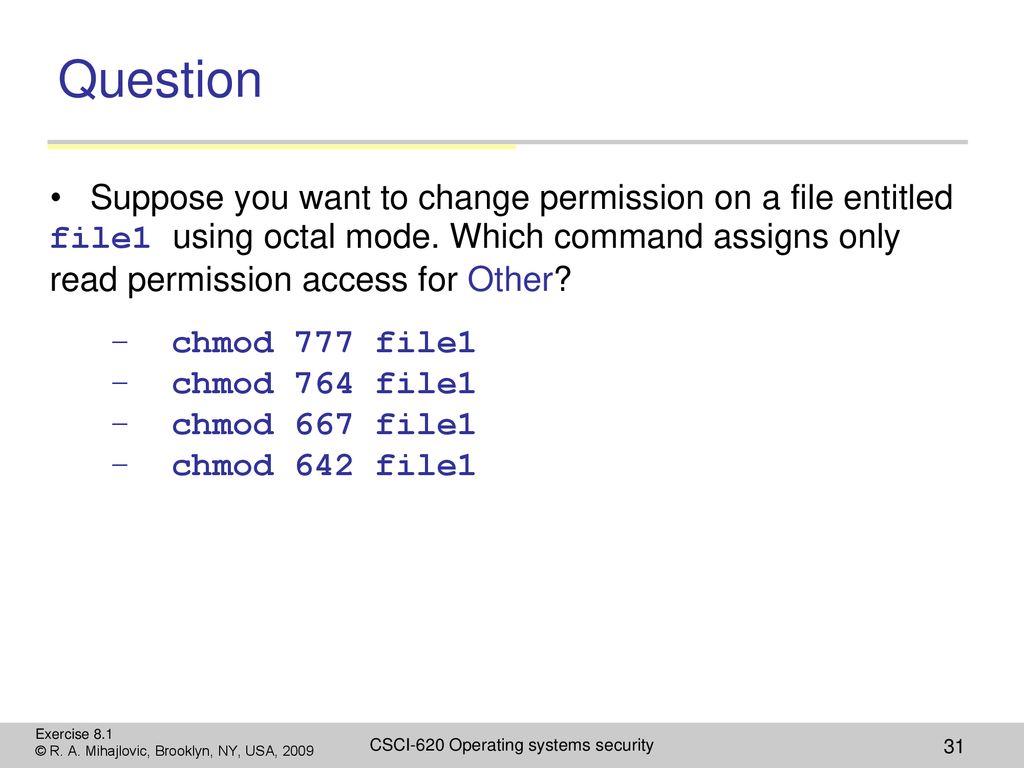


File Security And Access Control Ppt Download



Apply Chmod To A Folder Its Contents Sub Directories Wtmatter
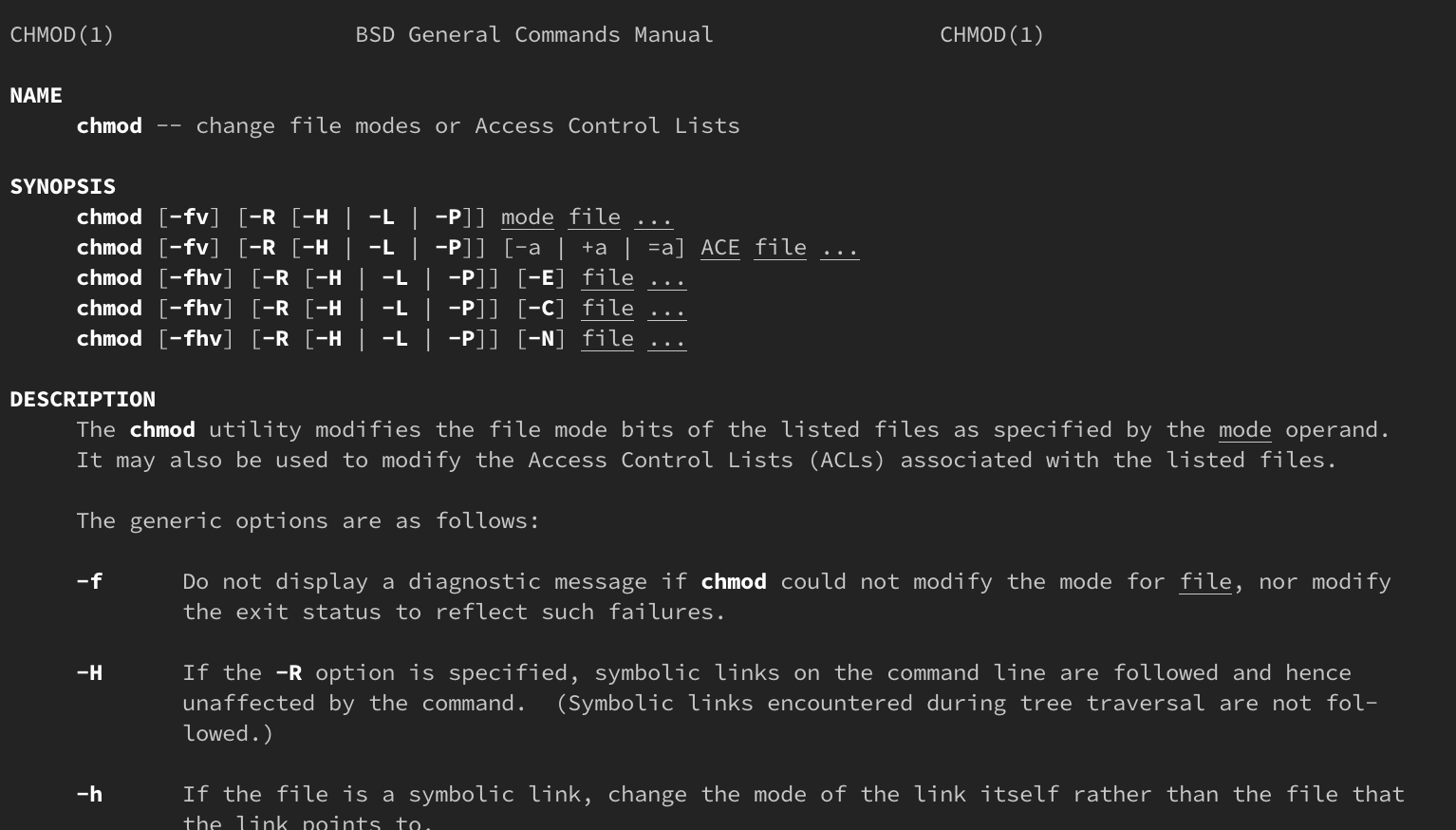


How Do Linux Permissions Work



Devrant A Fun Community For Developers To Connect Over Code Tech Life As A Programmer



Chmod 555



Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier



How To Use The Terminal Chmod Command Demystified And Put To Use Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿